How to Troubleshoot Failed MSI Installs
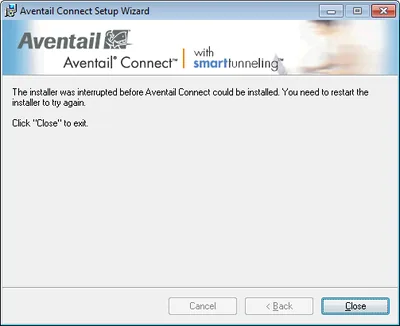
I was given the Aventail VPN client software to install on a customer’s Windows 7 x64 computer. That failed miserably. Here is what I did to find the root cause of the problem.
Troubleshooting
| Tag 21 posts | |
| 64-Bit Windows (X64)Tips and ToolsConferencesHelge's ToolsMiscellaneousPerformance/SizingPhotography |